|
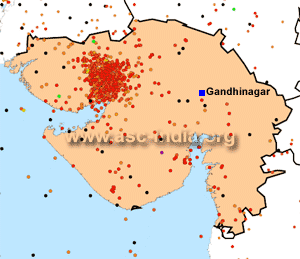 State
- Gujarat, India State
- Gujarat, India
Capital
- Gandhinagar
State Population
-
50,596,992
(2001)
Million+ Cities
Ahmedabad -
pop. 3,515,361
Surat - pop.
2,433,787
Vadodara - pop.
1,306,035
Population per
district (Top 5)
Ahmedabad
- pop. 5,816,519
Surat - pop. 4,995,174
Vadodara (Baroda) - pop. 3,641,802
Rajkot - pop. 3,169,881
Banas Kantha - pop. 2,504,244
Earthquake History
In peninsula
India the state of Gujarat, along with Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh,
has suffered from frequent earthquakes, both deadly and damaging,
although not located on or near any plate boundaries. All the
earthquakes here, as in all of peninsula India, are intraplate events.
Several active faults have been identified (3)
in the state. In the Rann of Kachchh, close to the Pakistani border,
lies the Allahbund Fault. Lying almost parallel to it, but further
south, near Pachham and Khudar Islands in the Great Rann lie the Nagar
Parkar, Island Belt and the Banni Faults. Along the spine of the
Kachchh mainland, runs the Kachchh Mainland Fault. Other faults run
along the coasts of Kachchh and Saurashtra, the Narmada and Tapti
Deltas and in the northern Kathiawar peninsula. The Cambay Graben,
runs from the Gulf of Khambat upto the border with Pakistan,
north-west of Radhanpur. However, it must be stated that proximity to
faults does not necessarily translate into a higher hazard as compared
to areas located further away, as damage from earthquakes depends on
numerous factors such as subsurface geology as well as adherence to
the building codes.
Seismic Hazard
The seismic hazard map of India was
updated in 2000 (6) by the Bureau of
Indian Standards (BIS). There are no changes in the new map as compared to the
BIS 1984 map for the state of Gujarat. Most of the district of Kachchh lies in
Zone V. MSK intensities in excess of IX can be expected in this district. Some
parts of eastern Kachchh, along with western sections of Banaskantha and Mehsana
districts and northern parts of Jamnagar, Rajkot and Surendranagar districts lie
in Zone IV. The maximum MSK expected here would be VIII. All the remaining
districts lie in Zone III, where the maximum intensity expected would be around
MSK VII. It must be noted that BIS estimates
the hazard, based in part, on previous known earthquakes. Since the earthquake
database in India is still incomplete, especially with regards to earthquakes
prior to the historical period (before 1800 A.D.), these zones offer a rough
guide of the earthquake hazard in any particular region and need to be regularly
updated
(See also:
GSHAP Hazard Map for Gujarat).
Largest Instrumented
Earthquake in Rajasthan
26 January 2001 -
Bhachau-Chobari (Bhuj) area, Gujarat, Mw 7.7
(14)
23.442
N, 70.310
E, D=16.0
kms, OT=03:16:40
UTC (14)
A
major earthquake struck Gujarat at
08:46 AM local time resulting in close to 13,823 deaths and extensive damage to
property in Gujarat. Damage to a lesser extent also
occurred in the adjoining states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan in
India and in Sindh province, Pakistan.
Significant
Earthquakes in Rajasthan
The following list briefly outlines known earthquakes in this region
which either had observed intensities of
VI
or higher (historical
events) or had known magnitudes of
M5.5 or more
(instrumented events). General locations are provided for historical events for
which "generalized" epicentral co-ordinates are available.
Some events which were significant for other reasons are also included.
This list will be updated whenever newer information is available. Please note
that Magnitude and Intensity are NOT THE SAME. All events are within the state
or union territory covered on this page unless stated otherwise.
Acronyms Used:
D=Depth,
OT=Origin
Time, Mw=Moment
Magnitude, Ms=Surface
Wave magnitude,
Mb=Body
Wave Magnitude, ML=Local
Magnitude, M?=Magnitude
Type unknown
|
This listing will be modified
without notice. Please check back for the latest version
when using it elsewhere. Additionally, please
reproduce using appropriate
CITATIONS/CREDITS. |
29 August 1636 -
Surat area, Gujarat.
Maximum observed intensity III (7).
Felt distinctly for around 30 seconds (7).
February 1705 -
Bhavnagar-Gogha area, Gujarat.
Maximum observed intensity XI (7).
Vivid descriptions of ground fissures indicate a lower intensity value of VIII
or IX.
16 June 1819 -
Rann of Kachchh, Gujarat, Mw 8.2 (1).
23.60
N, 69.60
E (3)
About 2,000 people were killed and dozens of towns and
villages were destroyed in Kachchh and adjoining parts of southern Pakistan. The
earthquake resulted in great surface deformation including a 90-kilometres
stretch of land which was uplifted about several metres, called the Allah Bund. The
shock was felt throughout the Sub-continent as far as Chennai and Kolkata.
13 August 1821 -
Kheda-Nadiad area, Gujarat.
22.700
N, 72.700
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity V (14).
This area is located to the south-east of Ahmedabad.
20 July 1828 -
Bhuj-Anjar area, Gujarat.
23.200
N, 69.900
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VI (14).
26 April 1848
- Disa area, Gujarat.
24.400
N, 72.200 E
(3)
Maximum observed intensity VII (3).
This is often referred to as the Mt. Abu earthquake.
29 April 1864
- Dewan-Khambat area, Gujarat.
22.300
N, 72.800 E
(14)
Maximum observed intensity VII (14).
This area is located to the
west of Vadodara.
14 April 1872
- Bhavnagar area, Gujarat.
21.767 N,
72.233 E (15)
Maximum observed intensity VI (15).
14 January 1903 -
Kunria area, Gujarat, Ms 6.0 (3).
24.000
N, 70.000
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VII (14).
This area is located to the north-east of Bhuj in the Rann of Kachchh.
15 August 1906
- North of Bakhasar, Rajasthan, Mw 6.2 (18)
27.500 N, 70.250 E,
10:43:56.0 UTC (18)
Felt widely along the Indo-Pakistan border, Sindh, and Gujarat. It was felt for
several seconds in Rajputana, Jodhpur, Ahmedabad and around the Gulf of Khambat.
It was felt at Mirpur, Pakistan.
12 July 1907
- Tharpakar, Pakistan, Mw 5.6 (18)
25.000 N, 70.000 E,
17:20 UTC (18)
Maximum
observed intensity VI (14).
Felt
in Sindh, Pakistan and at Ahmedabad and Jodhpur, India.
21
April 1919 - Hebatpur-Bhavnagar area,
Gujarat.
22.000 N, 72.000 E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VIII (14).
20 July 1935
- Gulf of Khambat, Gujarat.
21.000
N, 72.400
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VII (14).
This area is located to the
west of Surat.
June 1938 -
Jhinjuwada-Vadgam area, Gujarat.
23.300
N, 71.700
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VI (14).
This area is located to the west of Ahmedabad.
14 July 1938
- Dhandhulka-Limbdi area, Gujarat.
22.400
N, 71.800
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VI (14).
This area is located to the
south-west of
Ahmedabad.
19 July 1938
- Dhandhulka-Limbdi area, Gujarat.
22.400
N, 71.800
E (2)
Maximum observed intensity VI (2).
This area is located to the
south-west of Ahmedabad.
23 July 1938
- Dhandhulka-Limbdi area, Gujarat.
22.400
N, 71.800
E (14)
Maximum observed intensity VII (14).
Felt at Rajkot, Morbi and Vikramgad (9).
This earthquake is also refered to as the Paliyad earthquake. This
area is located to the
south-west of Ahmedabad.
1940 -
Umia-Luna area, Gujarat, Ms 5.8 (3).
23.700
N, 69.100
E (3)
This area is located to the
east
of Lakhpat and to the west of Bhuj.
This
earthquake might be the same as the following event reported in
northern Saurashtra for which no magnitude is available.
31 October 1940 -
Dhrol-Jamnagar area, Gujarat.
22.500
N, 70.400
E (2)
Maximum observed intensity VI (2).
This earthquake might be the same as the previous event reported in
Kachchh for which no date (day and month) or origin times are
available.
27
November 1945 -
Off the Makran coast, Pakistan, Mw
8.0
(10)
24.500 N, 63.000
E, D=025.0 kms,
OT=21:56 UTC (10)
At least 2000 people killed in southern Pakistan and neighbouring
Iran. Tsunamis with heights of 12 meters struck the Makran coast.
Damage also occurred at Ormara. Tsunamis with
heights in excess of 6 metres were also observed in Kachchh.
14 June 1950 -
Tharad-Jhajham area, Gujarat, M? 5.6 (14).
24.000 N, 71.200 E (14)
Maximum observed intensity V (14).
21 July 1956 -
Bhadreshwar-Anjar area, Gujarat, Mw 6.0 (11).
23.000 N, 70.000 E, OT=15:32:25 UTC (2)
Maximum observed intensity IX (3).
115 people were killed and hundreds injured. 1,350 buildings
were destroyed (3)
at Anjar alone. Felt
(3)
over an area with a radius of 330 kilometres
and as far as Hyderabad (Pakistan).
01 September 1962 -
Khed Brahma-Vadali area, Gujarat, Ms 5.0 (3).
23.000 N, 73.000
E (3)
This event was located north of Himatnagar in
north Gujarat, along the border with Rajasthan.
23 March 1970
- Ankleshwar-Bharuch area, Gujarat, Mw 5.4 (11).
21.600 N, 72.960 E, D=008.0 kms, OT=01:53:01 UTC
(3)
Maximum observed intensity VII (3).
26 people were killed and 200 people were injured in this
earthquake, in Bharuch and the neighbouring villages. There was
heavy damage (3)
in Bharuch city. Ground fissures
(3)
were reported over
a distance of 20 kilometres and large
amounts of water and sand was emitted from them.
The quake was also felt (3)
in Ankleshwar, Bhavnagar, Surat
and Vadodara.
26 March 1975 -
Arabian Sea, Mb 5.2 (17).
19.754 N, 68.398 E, D=033.0 kms, OT=16:19:19 UTC
(17)
This earthquake was located 245 kilometres
south-west of Porbander and 475 kilometres west of Mumbai.
24 August 1993
- Arabian Sea, Mb 4.9 (3).
20.700 E, 71.440 E,
D=029.0 kms, OT=17:47:30 UTC (3)
This event was located in the Gulf of Khambat, to
the west of Surat, Gujarat. This earthquake was felt widely
in south-eastern Gujarat and parts of coastal Maharashtra. In
Gujarat, people rushed out into the open at Ankleshwar, Bardoli,
Bharuch and Bulsar. It was felt strongly (MM V) at Rajula. It was
also felt (MM IV) at Amreli, Bhavnagar and Surat. In Maharashtra, it
was felt (MM III) in Mumbai. Reports of tremors were received from
Bandra, Chembur, Juhu, Kandivili and Prabhadevi. The shock was
perceived over an area with a radius of
250 kilometres.
12 September 2000
- Bhavnagar area, Gujarat, ML
3.8 (5)
21.680
N, 72.123 E, OT=00:53:27
UTC (5)
1 person was injured and scores of buildings were damaged in the
largest shock in a seismic swarm that
began in 1999 and began to peak in August 2000.
Most of the recorded events were below magnitude 3.0 but due to the
fact that they were shallow in origin and also because they were
located very close to a densely populated area (Bhavnagar) most of
them were felt strongly enough to cause panic. Many people left
Bhavnagar during the swarm and transportation services heading out
of the city were swamped by fleeing residents.
26
January 2001 -
Bhachau-Chobari (Bhuj) area, Gujarat, Mw 7.7
(5)
23.442
N, 70.310
E, D=16.0
kms, OT=03:16:40
UTC (5)
A
major earthquake struck Gujarat at
08:46 AM local time resulting in close to 13,823 deaths and extensive damage to
property in Gujarat. Damage to a lesser extent also
occurred in the adjoining states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan in
India and in Sindh province, Pakistan.
28 January 2001
-
Suvi-Rapar area, Gujarat, Mw 5.8 (5)
23.532
N, 70.598
E, D=10.0
kms, OT=01:02:10
UTC (5)
A
moderate to strong aftershock struck
Gujarat, at 06:32 AM local time causing considerable panic in
Gujarat, India. Tremors were also felt in adjoining
parts of Maharashtra & Rajasthan.
08 February
2001 -
Suvi-Chobari area, Gujarat, ML 5.1 (5)
23.693
N, 70.400 E,
OT=16:54:42 UTC (5)
Many injured at Ahmedabad after jumping from
buildings in panic.
05 August 2003
-
Suvi area, Gujarat, Mw 5.0 (5)
23.640
N, 70.230 E,
D=010.0 kms, OT=11:08:03 UTC
(5)
A
moderate earthquake
struck Gujarat, India, on 5 August
2003 at 16:38 PM
local time causing minor damage in eastern Kachchh and
considerable panic elsewhere Gujarat,
India. The earthquake had a
magnitude of Mw=5.0.
07 March 2006
-
Mouna area, Gujarat, Mw 5.5 (10)
23.768
N, 70.853 E,
D=018.0 kms, OT=10:20:46 UTC
(10)
A
moderate earthquake struck
the eastern Great Rann in Gujarat, India,
on 7 March 2006 at 23:50 PM local time causing a
few injuries and minor damage to property in Rapar taluka, India.
The earthquake had a magnitude of
Mw=5.5 and is the strongest earthquake in this
immediate region since a Mw=5.8 aftershock on 28 January 2001 from
the Bhuj earthquake in January 2001.
06 April 2006
-
Vondh area, Gujarat, Mw 5.5 (10)
23.308
N, 70.444 E,
D=010.1 kms, OT=17:59:17 UTC
(10)
A
moderate earthquake struck
the Kachchh region in
Gujarat, India, on 6 April 2006 at 23:29
PM local time causing minor damage to property.
The earthquake had a magnitude of
Mw=5.5. This is second event of this
magnitude in this region since a Mw=5.5 on 7 March 2006.
08 April 2007
-
Gandhidham area, Gujarat, Mb 4.2
23.083
N, 70.187 E,
D=010.0 kms, OT=16:20:13 UTC
A
light earthquake struck
the Kachchh region in Gujarat, India, on 8
April 2007 at 21:50 PM local time. It had a magnitude of
Mb=4.2 and was felt in parts of Kachchh and
Saurashtra in the state of Gujarat.
6
November 2007
-
Sasan Gir region, Gujarat (multiple
events)
Two moderates
earthquake occurred in the vicinity of the
Gir National Park and adjoining parts of Saurashtra in
Gujarat, India, on 6
November 2007 at 05:58 AM and 15:08
PM local time. Both had preliminary
magnitudes of Mb=5.1. They were felt in
many parts of the state of Gujarat and resulted
in at least one death.
13 August 2011
-
Dudhai-Bhachau area, Gujarat, M?=4.2
23.300
N, 70.200 E,
D=033.0 kms, OT=02:59:14 UTC
A light
earthquake occurred in the Kachchh region of Gujarat, India,
on 13 August 2011 at 08:29 AM
local time in India. It had a magnitude of M?=4.2 and was
widely felt in Kachchh and Saurashtra causing panic.
20 October 2011
-
Sasan Gir region, Gujarat, Mw=5.0
21.181
N, 70.540 E,
D=015.5 kms, OT=17:18:25 UTC
A moderate
earthquake occurred in the Gir
National Park region in Gujarat's Saurashtra region, India,
on 20 October 2011 at 22:48 PM
local time in India. It had a magnitude of Mw=5.0 and was
widely in the Kathiawar peninsula as well as far as Mumbai. Several
injuries and considerable damage occurred in Junagarh district.
12 November 2011
-
Sasan Gir region, Gujarat, ML=4.3
21.064
N, 70.519 E,
D=009.9 kms, OT=07:01:51 UTC
A light
earthquake occurred in the Gir National Park region
in
Gujarat's Saurashtra region, India, on
12 November 2011
at 12:31:51 PM local
time in India. It had a magnitude of ML=4.3. Three people was
injured and
damage occurred in the districts of Amreli and Junagadh in Gujarat. This event is the
strongest aftershock from a
Mw=5.0 earthquake in the same region in
October 2011. |